(gdb) start Temporary breakpoint 1 at 0x8048446: file test.cpp, line 2. Starting program. GDB stands for GNU Project Debugger and is a powerful debugging tool for C (along with other languages like C).It helps you to poke around inside your C programs while they are executing and also allows you to see what exactly happens when your program crashes. Mar 01, 2019 GDB stands for GNU Project Debugger and is a powerful debugging tool for C (along with other languages like C).It helps you to poke around inside your C programs while they are executing and also allows you to see what exactly happens when your program crashes.
One of the top 100 Geospatial firms in the U.S.
The principals and employees at GdB work on projects within the transportation, environmental, energy, infrastructure, recreation, and educational industries. Public clients include agencies at the state, county, city, and local levels. Private clients include design professionals, contractors, developers, and the general public.
161 Maiden Lane – 58 Story Wall Scan
Manhattan, NY
Gayron de Bruin Land Surveying and Engineering, PC performed 3D Laser Scanning services of a 58-story building under construction at 161 Maiden Lane, New York, NY.
Four independent control networks were set, each relating to a different side of the building to determine if the building was leaning. Independent scans were performed on the full extent of the building in question on rooftops where the building was visible as well as from the streets in the immediate vicinity. GdB utilized a Leica P50 3D Laser Scanner to perform this detailed work.
Deliverables included the registered point cloud and an AutoCAD 3D file containing polylines representing the perimeter of each of the 58 floor slabs. The CAD file also included offset dimensions on all faces of each floor.
This project was delivered on time and within budget.
Honk Falls Dam
Napanoch, NY
At the Honk Falls Dam in Napanoch, NY, GdB provided comprehensive field surveys, topographic and utility mapping for future design efforts. GdB used a combination of traditional survey methods as well as Aerial Drone Photography and Baythmetric surveys to complete this task.
Carrel Boulevard Drainage Improvements
Oceanside, NY
Gayron de Bruin Land Surveying and Engineering, PC was hired as a subconsultant to perform surveying and mapping services to Town of Hempstead specifications which included topographic, boundary and subsurface utility mapping as well as storm water and sanitary structure investigations within the specified project scope.
Following Town of Hempstead surveying and mapping standards, elevations were taken at 25’ cross sections for roughly 4,675 linear feet of roadway. All planimetric features and topography was mapped up to the face of the houses, which included house corners, first floor elevations, garage floors, top and bottom of entry way steps, window wells and planting areas as well as any and all features that may be impacted by regrading and raising the road. GdB used a combination of traditional ground survey and terrestrial LiDAR to optimize our time spent on this task.
Contact Us
GdB Long Island
88 Duryea Road
Melville, NY 11747
Office: 516.579.3111
GdB Honeoye Falls
12 North Main Street, Suite 100
Honeoye Falls, NY 14472
Office: 585.484.8100
GNU or GDB debugger is an application for finding out how your C or C++ program runs or for analyzing the moment the program crashes. You can perform many useful tasks with GDB: run the program, stop the program under specific conditions, analyze the situation, make modifications, and test new changes.
Contents
More on the GDB debugger
You can use GDB as a C++ debugger if a program is written with the GNU compiler and the -g flag. By debugging with GDB, you can catch errors and solve them before they cause severe issues.
Tip: a quick option is using the onlineGDB debugger, which lets you compile and analyze C++ code online without having to download the debugger to your operating system.
Here is how the onlineGDB debugger looks:
Preparing the GDB debugger for use
The first step of learning how to use GDB for C++ debugging is to compile the C++ code with the -g flag:
The next step is calling the GDB to start the debugging process for the program you wish to analyze:
Note: for the next functions, the (gdb) part of the command appears automatically.

The code above opens this C++ debugger but does not run the program. There are several ways of running the program you have opened. First, you can execute it with run command:
You can pass arguments if the program needs some command-line arguments to be passed to it:
Debugging with GDB lets you investigate the core file as well. The core file contains information about when a program crashed.
Note: by typing the help command, you will learn more about the commands to use in the GDB debugger.
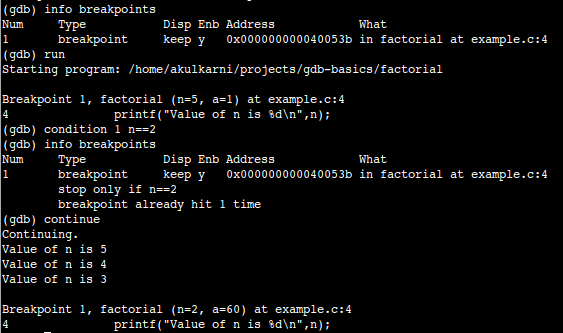
Setting breakpoints to stop the execution of a program
You can debug your C++ program more efficiently if you use breakpoints. Breakpoints refer to instructions that stop the execution at specific moments. For instance, you should set breakpoints in places you suspect to be problematic.
It is possible to set breakpoints in two ways:
- Setting a line at which execution stops.
- Setting a function name to stop execution at.
Note: it is a common practice to set breakpoints before running the program.
The following example sets a breakpoint at the start of the main function:
This example sets a breakpoint at a specific line (20):
This example adds a breakpoint at the beginning of a class member function:
This example lists all of the breakpoints:
The following example deletes a breakpoint at line 20:
Note: the GDB debugger accepts abbreviations of commands. Therefore, you can use b instead of break or p instead of print.
Running the program slowly
You might need to execute a program slowly, moving from one function to another. There are two ways of making the program run step-by-step.
next executes the current command, stops, and displays the next function in line for execution.

step: executes the current command. In cases when it is a function call, it breaks at the beginning of that method. You can use it for looking for errors in nested code.
Printing values of variables and expressions
With the GDB debugger, you can check the values of variables during specific moments of the execution. You will use the print command for this task. It is possible to print more complicated expressions, type casts, call functions, etc.
The possible syntax for using print:
print <exp>: to get values of expressions.print /x <exp>: to get the value of expressions in hexadecimal.print /t <exp>: to get the value of expressions in binary.print /d <exp>: to get the value of expressions as unsigned int format.print /c <exp>: to get the value of expressions as signed int format.
Using where and frame commands
During analysis of code, you might need to check which function currently runs.
Gdb Tutorial
By typing the where command, you will learn these things:
- The name of the currently running function.
- The name of the file in which the function runs.
- The number of the line in which the function is.
- The name of the function that called the current function.
- The arguments the current function had.
- If it is a call chain, you will see all of them.
You can analyze the values of variables local to the calling function (or other function in the stack). The frame command instructs the GDB debugger to work on the specific stack frame or the one you are currently at.
Tip: the stack frame shows the sequence of function calls.
frame <frame-num>: sets the current stack frame to the indicated as<frame-num>.info frame: displays the state of the current stack frame.
Commands to use in the GDB debugger
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| help | Provides information about a topic or commands you can use |
| file | Indicates which file to debug |
| run | Executes the program under GDB |
| break | Adds breakpoints to stop the program execution temporary |
| delete | Deletes breakpoints |
| clear | Deletes breakpoints for a specific function |
| continue | Resets the program after a breakpoint triggers |
| step | Runs the current source line and stops before executing the next one |
| next | Runs the current source line. However, if the line is a function call, the debugger will fully execute the function before the execution stops again |
| until | Runs the current source line. If you are at the beginning of a loop, the debugger runs until the loop ends |
| list | Prints a certain list from the source code |
| Prints values of certain expressions |
Welcome To Guide Dogs For The Blind | Guide Dogs For The Blind
Other C++ debuggers to consider
GDB Tutorial: Essential GDB Tips To Learn Debugging
- Visual Studio has an integrated C++ debugger that lets you analyze code on the most popular operating systems such as Linux, Windows, macOS.
- LLDB debugger is a modern debugger that has reusable components that employ libraries from LLVM.
- WinDbg is a debugger for the Microsoft Windows operating systems.